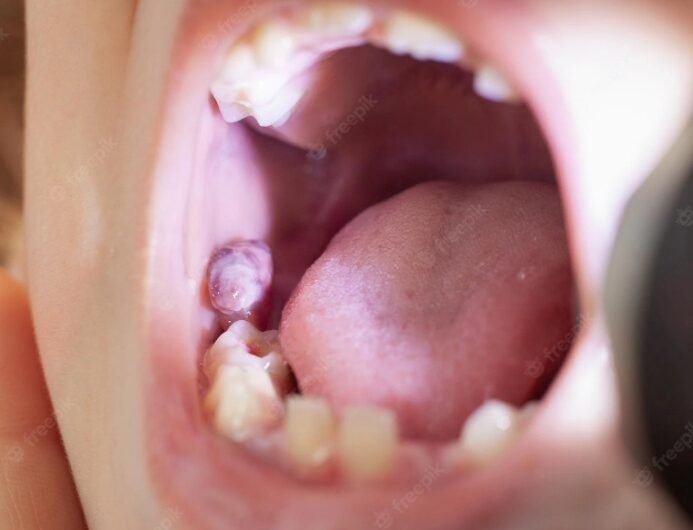
A broken tooth root that remains lodged in the gum can be a distressing dental issue, potentially causing pain, infection, and complications. In this in-depth guide, we will explore what to do if your tooth breaks and the root is still in the gum, the causes of broken tooth roots, symptoms of a broken tooth root, the risks of leaving a broken tooth root in the gum, how to remove a broken tooth root, recovery after tooth root removal, and tips for preventing broken tooth roots.
What to Do if Your Tooth Breaks and the Root Is Still in the Gum:
A broken tooth root is a situation that should be addressed promptly to prevent further complications. Here are the steps to take if your tooth breaks and the root remains in the gum:
- Rinse your mouth: Gently rinse your mouth with warm water to remove any debris or blood. Be careful not to use hot or cold water, as extreme temperatures can worsen sensitivity.
- Apply gauze: If there is bleeding, apply a clean piece of gauze to the affected area and apply gentle pressure to stop the bleeding.
- Preserve the broken tooth fragment: If you can, retrieve and preserve the broken tooth fragment. Place it in a container with milk or your saliva to keep it moist.
- Contact your dentist: Schedule an emergency appointment with your dentist as soon as possible. They will assess the situation and determine the best course of action.
- Over-the-counter pain relief: If you experience pain or discomfort, you can take over-the-counter pain relievers as directed by your dentist or healthcare provider.
Causes of Broken Tooth Roots:
A broken tooth root can occur due to various factors, including:
- Trauma: A blow to the face or mouth can lead to a fractured tooth root.
- Advanced decay: Severe tooth decay can weaken the tooth structure to the point where it breaks, leaving the root behind.
- Chewing hard objects: Biting down on hard objects like ice, nuts, or hard candy can cause a tooth to break.
- Weakened tooth: Teeth weakened by large fillings or root canal treatment may be more prone to breaking.
- Age: Over time, teeth can become more brittle, making them more susceptible to fractures.
Symptoms of a Broken Tooth Root:
Recognizing the symptoms of a broken tooth root is essential for seeking prompt treatment. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Pain: You may experience persistent or intermittent pain in the affected tooth or gum.
- Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures, especially when consuming food or beverages.
- Swelling: Swelling and tenderness in the gum tissue around the broken tooth root.
- Visible damage: In some cases, you may see visible damage to the tooth, such as a chip or fracture.
- Discomfort when chewing: Pain or discomfort while chewing or biting down.
- Infection: In severe cases, a broken tooth root can lead to infection, causing pus, foul taste, and bad breath.
Risks of Leaving a Broken Tooth Root in the Gum:
Leaving a broken tooth root in the gum can lead to various risks and complications, including:
- Infection: The presence of a broken tooth root can create an entry point for bacteria, leading to a localized or systemic infection.
- Pain and discomfort: Persistent pain and discomfort can affect your quality of life.
- Abscess: An untreated infection can progress to an abscess, a pocket of pus that can be extremely painful.
- Gum disease: The gum tissue around the broken tooth root may become inflamed, leading to periodontal disease.
- Tooth misalignment: Nearby teeth may shift or move to compensate for the missing tooth, causing alignment issues.
- Bone loss: Prolonged presence of a broken tooth root can lead to bone loss in the jaw.
How to Remove a Broken Tooth Root:
Removing a broken tooth root typically requires dental intervention. Here’s what you can expect during the removal process:
- Diagnosis: Your dentist will examine the broken tooth root using dental X-rays and clinical evaluation to determine the extent of the damage.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia will be administered to numb the affected area, ensuring a pain-free procedure.
- Tooth extraction: If the remaining tooth structure is viable, the dentist may attempt to extract the root fragment. If the tooth is extensively damaged, extraction of the entire tooth may be necessary.
- Surgical removal: In some cases, especially if the root is deeply embedded or there are complications, a surgical procedure may be required to access and remove the broken tooth root.
- Closure: Once the root fragment is successfully removed, the dentist will close the area with stitches if needed.
- Follow-up: Your dentist will provide post-operative instructions, including guidelines for pain management and wound care.
Recovery After Tooth Root Removal:
Recovery after tooth root removal involves taking care of the extraction site and following your dentist’s recommendations:
- Pain management: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications can help manage post-operative discomfort.
- Diet modification: Stick to a soft diet for a few days, gradually reintroducing solid foods as advised by your dentist.
- Oral hygiene: Follow your dentist’s instructions for keeping the extraction site clean, which may include gentle rinsing with saltwater.
- Avoiding irritants: Avoid smoking and consuming alcohol during the healing process, as these can slow down healing and increase the risk of complications.
- Follow-up appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your dentist to ensure proper healing and monitor the extraction site.
Preventing Broken Tooth Roots:
Preventing broken tooth roots involves practicing good oral hygiene and adopting protective measures:
- Regular dental check-ups: Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings to detect and address potential dental issues.
- Avoid hard foods: Be cautious when consuming hard or crunchy foods to prevent dental fractures.
- Use protective gear: If you engage in contact sports or activities that carry a risk of facial trauma, wear a mouthguard to protect your teeth and roots.
- Address dental decay: Promptly treat dental cavities and undergo necessary dental procedures to strengthen weakened teeth.
- Avoid excessive force: Be mindful of how you use your teeth, avoiding habits like biting fingernails or opening objects with your teeth.
In conclusion, a broken tooth root left in the gum can lead to various dental issues and complications. It’s crucial to seek prompt dental care if you suspect a broken tooth root to prevent infection and alleviate discomfort. Dental professionals are equipped to diagnose, treat, and guide you through the recovery process, ensuring the best possible outcome for your oral health. Additionally, preventive measures can reduce the risk of broken tooth roots, allowing you to maintain a healthy and functional smile.