Learn about the potential causes and effective management of swollen gum behind back tooth no wisdom teeth, a common ailment. A dental professional will help you identify the root cause and devise a treatment plan. With our help, relief is just a step away.
Swollen gum behind back tooth no wisdom teeth:
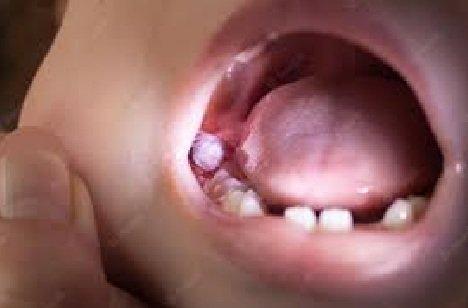
An occurrence of swollen gums situated behind a posterior tooth can stem from multiple potential etiologies. These include periodontal disease, dental caries or even trauma. In the absence of wisdom teeth, the swelling is more likely to be linked to an issue related to the tooth itself.
To establish the underlying cause of the inflammation and receive appropriate management, it is crucial to consult with a dental professional. They will carry out an oral examination, take radiographs if necessary, and provide recommendations for treatment.
Meanwhile, to alleviate symptoms and prevent contamination, it is advisable to take over-the-counter analgesics and maintain a rigorous oral hygiene routine, such as brushing and interdental cleaning on a regular basis.
pericoronitis:
Pericoronitis is a pathological condition characterized by the inflammation of the soft tissues that encase a tooth that has not fully emerged. This condition is primarily associated with third molars (wisdom teeth) and it is caused by the accumulation of bacteria and food debris underneath the flap of tissue that covers the tooth. The symptoms of pericoronitis are diverse and include orodynia, edema, trismus, pyrexia, halitosis and a metallic taste in the oral cavity. Left untreated, pericoronitis can lead to severe complications such as the formation of abscesses and the dissemination of the infection. The management of pericoronitis typically involves debridement of the affected area, administration of antibiotics, and resolution of any underlying issues with the tooth, such as extraction or surgical interventio
Gum pain in back of mouth not wisdom teeth:
the causes and effective management of gum pain in back of mouth not wisdom teeth are many . This discomfort can stem from various etiologies such as:
- periodontitis
- dental : A pocket of pus that forms around the end of a tooth or in the gums.
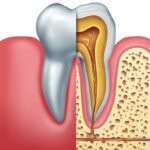
- caries:Decay of the tooth that can cause sensitivity and pain.
- Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses that can cause referred pain to the back of the mouth.
- tumors or cysts: Abnormal growths that can cause pain and swelling.
A dental professional will help you identify the root cause and devise a treatment plan, whether it be through x-ray examination or other diagnostic measures.
Gum hurts where wisdom teeth was removed years ago:
investigating the causes of gum pain where wisdom teeth was removed years ago nees an expert
Alveolitis sicca: is a condition that occurs when the blood clot that is formed during the healing process after tooth extraction is dislodged or dissolves, exposing the underlying bone and nerves to infection.
Neural injury :can also occur due to damage to the nerves in the area during the extraction, leading to pain, paresthesia or anesthesia
contamination: Contamination, on the other hand, can occur if bacteria are not properly removed or if the wound is not kept clean, leading to an infection
fibrosis; is the formation of fibrous tissue that can cause pain, discomfort or a feeling of pressure in the area
It is essential to consult with a dental professional or an oral surgeon to determine the cause of the pain and to receive appropriate treatment. They will be able to examine the area and recommend a course of action.”
How to treat swollen gums near wisdom teeth:
Swollen gums near wisdom teeth can be a result of a variety of underlying causes, and the appropriate treatment will depend on the specific condition. However, how to treat swollen gums near wisdom teeth? is a very commun question , some common treatment options include:
- Dental prophylaxis: A thorough oral cleaning, including scaling and root planing, can help remove plaque and bacteria that contribute to inflammation and infection.
- Medication therapy: Antibiotics may be prescribed to help clear any infection and reduce inflammation. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can also be used to alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Thermotherapy: Applying warm compresses to the affected area can help increase blood flow and reduce pain and inflammation.
- Surgical intervention: In some cases, surgical removal of the affected tooth or tissue may be necessary. This can include extraction of the wisdom tooth, periodontal surgery to remove infected tissue, or a combination of both.
- Orthodontic therapy: Crowding of the teeth can make it difficult to maintain good oral hygiene and may lead to gum inflammation. In such cases, orthodontic therapy may be necessary to straighten teeth and create enough space to brush and floss properly.
It is important to visit a dental professional to determine the cause of the swollen gums and to receive appropriate treatment. They will be able to examine the area, take X-rays if needed, and recommend a course of action. It’s also important to maintain good oral hygiene practices and avoid smoking or tobacco use, as these can worsen the condition.
Additionally, a healthy diet rich in nutrients, vitamins and minerals can help prevent gum inflammation and improve overall oral health. Drinking plenty of water can also aid in preventing dryness and maintaining a healthy oral environment. It is also essential to schedule regular dental checkups and cleanings to monitor the condition and prevent any.